A Complete Guide to English Adverbs | Types, Usage and Examples
Home » Parts of Speech » A Complete Guide to English Adverbs | Types, Usage and Examples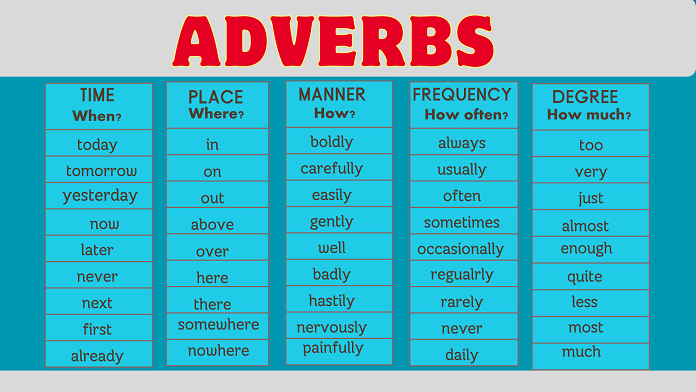
Adverbs serve as a powerful tool, allowing the modification of verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs to create sentences that are both nuanced and descriptive. Adverbs play an important role in conveying manner (the way something happens), degree (the extent to which it occurs), place (where it takes place), and time (when it happens).
This article comprehensively examines adverbs, unravelling their diverse types, functions, and applications. Whether you are an experienced writer or new to writing. This article will provide you with the requisite knowledge and skill to use adverbs effectively and boost your writing to a higher standard.
Adverbs Key Points
- Adverbs commonly modify adjectives, verbs, and other adverbs to provide more detail.
- Not all adverbs end with “-ly,” making identification more challenging.
- Proper use of adverbs enhances fluency in English.
What Are Adverbs?
Definition of an Adverb
An adverb is an important part of speech to provide additional details about a verb, adjective, or another adverb within a sentence. It serves to convey information on how, where, when, to what extent, and with what frequency an action occurs. For instance, in the sentence ‘she runs quickly,’ the adverb quickly modifies the verb ‘runs,’ indicating the speed of the action.
Adverbs extend their influence beyond verbs and can also modify adjectives, contributing further information. For instance, in the sentence ‘he is quite fat,’ the adverb quite modifies the adjective ‘fat,’ intensifying its degree.
Moreover, adverbs can even extend their impact to an entire sentence. Consider the example ‘Luckily, I had enough money.’ Here, the adverb luckily modifies the entire sentence, conveying a sense of fortune.
While many adverbs typically end in -ly, exceptions exist. Take the adverb fast, for instance, which retains the same form as its adjective counterpart. In the sentence ‘This is a fast car,’ fast functions as an adjective, describing the car. However, in ‘This car can drive fast,’ fast becomes an adverb, elucidating the speed of the car.
Let’s explore additional examples of adverbs within sentences:
- My sister swims badly.
- The soccer match ended quickly.
- Fortunately, her friends were not late for my anniversary.
Adverbs with Verbs
Adverbs are typically used with verbs to explain how an action occurs, it is being used to answer the question of “How does something happen?” or “In what manner does it happen?” Examples showing this concept include:
- The music played softly in the background.
- She appeared sadly at the news.
In these instances, the adverbs respond to questions such as ‘How does the music play?’ and ‘How does she look at the news?’ In essence, when seeking to understand how an action is performed, an adverb serves this purpose.
It’s imperative to note that adverbs are incompatible with linking verbs, such as to smell, to feel, to seem, to appear, or to taste. For instance:
He smells horribly in the kitchen. (Incorrect)
In cases involving linking verbs, which necessitate describing what is taking place rather than how it’s happening, an adjective proves more fitting:
He smells horrible in the kitchen. (Correct)
Adverbs with Adjectives and Other Adverbs
Adverbs possess the ability to enhance the intensity and clarity of adjectives or other adverbs in a sentence. This is a great way to boost descriptive quality and provide a clearer indication of the subject matter.
For instance, consider the phrase “she runs fast.” The adjective here is fast, but with the use of an adverb, we can describe how fast she runs. Take a look at the sentence once it has been modified:
- She runs incredibly fast.
Here are additional examples of how an adverb can modify an adjective:
- His paintings are remarkably vibrant.
- The music was unexpectedly soothing.
- The journey was consistently enjoyable.
The other way to use an adverb to modify another adverb is below example:
- The car accelerated almost too quickly.
The adverb almost is being used to modify the adverb too quickly, and both are being used to modify the speed at which the car accelerates.
Using multiple adverbs together is possible, but caution is advised. Excessive adverbs can weaken a sentence, making it preferable to opt for one or two to enhance strength and clarity. Consider the example of a sentence overloaded with adverbs.:
- The movie ended quite abruptly, surprisingly loudly, and unexpectedly early.
I think you easily understand now what this sentence is trying to tell us, but the use of adverbs is a little too much.
Adverbs to Modify a Sentence
Adverbs can modify whole sentences, typically occurring at the start to convey an overall tone or feeling. Examples include:
- Ordinarily, students complete the assignment by the deadline.
- Fortuitously, the weather remained pleasant during the event.
- Curiously, the scientist observed unexpected results in the experiment.
Adverbs in Comparisons
Adverbs in comparisons involve the use of modifiers such as “more” or “most” with the adverb. Observe the progression in the following sentences:
- They worked efficiently.
- They worked more efficiently.
- They worked most efficiently.
Types of Adverbs and Examples
Adverbs have different types expressing different meanings and are distinguished by their functions. They inform us about how, where, when, to what extent, and with what frequency. The classification of adverbs is based on these functions.
Explore a list of adverbs in English, each type described with examples.
Adverbs of Frequency and Examples
Adverbs of frequency indicate the regularity of an action. Examples encompass: always, sometimes, often, normally, usually, occasionally, seldom, rarely, never, etc.
Example sentences:
- I always complete my assignments before the deadline.
- He rarely misses his morning jog.
- She occasionally indulges in dessert.
- We frequently organize team-building activities.
- He never fails to attend the weekly meetings.
- She hardly ever takes sick days.
- They sometimes collaborate on projects.
- He regularly updates his blog.
- She generally prefers reading in the evenings.
Adverbs of Manner Examples
Adverbs of manner explain how an action is executed. Examples encompass: joyfully, effectively, agonizingly, covertly, silently, serenely, meticulously, gradually, poorly, intently, effortlessly, adroitly, swiftly, etc.
Example sentences:
- She paints vividly on the canvas.
- He solved the puzzle methodically.
- They moved gracefully through the crowd.
- The alarm clock beeped loudly in the morning.
- She communicates softly during meetings.
- He cycles rapidly in the park.
- They executed the plan flawlessly.
- She organizes files efficiently at work.
- He explores the forest slowly to appreciate nature.
- They reacted enthusiastically to the news.
Adverbs of Time Examples
Adverbs of time specify when an action occurs. Examples encompass: currently, previously, imminently, subsequently, forthcoming, already, tonight, today, then, formerly, periodically, etc.
Example sentences:
- We are heading to the movies this evening.
- He rose early this dawn.
- They are reuniting with friends soon.
- She habitually studied late at night.
- He exercises in the gym daily.
- She completed her work recently.
- He is expected to arrive later today.
- They vacationed last month.
- She plans to visit the beach in the upcoming month.
Adverbs of Place Examples
Adverbs of place convey where an action transpires. Examples encompass: underneath, surrounding, indoors, above, outdoors, nearby, below, beneath, adjacent, subsequently, etc.
Example sentences:
- The cat is searching beneath the bed.
- We strolled around the park.
- The event took place indoors.
- The plane soars high above the clouds.
- Children are playing outdoors in the yard.
- The restaurant is situated in close proximity.
- The car is parked below ground.
- Examples are presented here.
- The boat navigated past the island.
Adverbs of Degree Examples
Adverbs of degree convey the extent of action or intensity. Examples comprise: exceedingly, reasonably, excessively, wholly, absolutely, remarkably, moderately, sufficiently, entirely, particularly, etc.
Example sentences:
- She is exceptionally intelligent.
- The party was moderately enjoyable.
- He spoke extremely softly.
- The movie was remarkably boring.
- The weather is absolutely wonderful.
- She was slightly nervous before her speech.
- He is completely exhausted after his workout.
- The cake is reasonably sweet, but not too sweet.
- The speaker is excessively loud; please turn it down.
Adverbs of Certainty Examples
Adverbs of certainty signify the level of assurance regarding an action. Examples encompass: assuredly, clearly, indubitably, doubtfully, undoubtedly, evidently, presumably, probably, undeniably, etc.
Example sentences:
- I am undoubtedly going to the party tonight.
- He is assuredly the best candidate for the job.
- They will certainly be there on time.
- I am indubitably sure that I locked the door.
- She is evidently upset about something.
- The plane will likely arrive on time.
- He is understandably nervous before starting practical life.
- The experiment clearly showed that the hypothesis was correct.
Adverbs of Attitude Examples
Adverbs of attitude enable the speaker to express sentiments or comments on the mood or disposition of the action. Examples encompass: contentedly, gratefully, frankly, hopefully, seriously, luckily, sadly, surprisingly, unbelievably, etc.
Example sentences:
- She smiled contentedly at her friend.
- He spoke politely to the customer.
- The teacher explained patiently to the student.
- She cried sadly after losing her purse.
- They argued angrily about the issue.
- The dog barked loudly at the stranger.
- She laughed nervously at his joke.
- The student answered confidently during the exam.
- The baby giggled happily at the toy.
Adverbs of Judgment Examples
Adverbs of judgment are utilized to assess or pass judgment on the action or event. Examples encompass: confidently, diligently, clearly, beautifully, recklessly, perfectly, impressively, eloquently, persuasively, skillfully, etc.
Example sentences:
- She spoke confidently during the presentation.
- He worked diligently on the project.
- The teacher explained the concept clearly.
- The singer performed beautifully on stage.
- They drove recklessly on the highway.
- The chef cooked the steak perfectly.
- The athlete ran impressively in the race.
- The company expressed its ideas eloquently in a corner meeting.
- The politician spoke persuasively during the debate.
- The artist painted the portrait skillfully.
Conjunctive Adverbs Examples
Conjunctive adverbs, also known as linking adverbs, serve to connect clauses or sentences, indicating relationships in terms of sequencing, contrast, cause, or effect. Examples include: further, comparatively, besides, conversely, equally, hence, namely, now, rather, undoubtedly, additionally, finally, anyway, certainly, elsewhere, in contrast, indeed, moreover, next, subsequently, thereafter, yet, nevertheless, etc.
Example sentences:
- I enjoy playing soccer; however, I can’t play today because it’s raining.
- She has a lot of work to do; therefore, she can’t come to the party tonight.
- The movie was extremely boring; nonetheless, we stayed until the end.
- I don’t like eating vegetables; in addition, I’m allergic to some of them.
- John is a skilled athlete; moreover, he’s also an excellent student.
- She loves to sing; similarly, his brother enjoys playing the guitar.
- The park was closed due to the snowstorm; hence, we had to take a different day.
Place of An Adverb
Front Position: before the subject
- Example: Quickly, she finished the race.
Mid Position: connected with the verb
- Example: He swam effortlessly across the pool.
End Position: at the end of the sentence
- Example: She finished the race quickly.
Special Note: The position of “only”
- Example: I only fed my bird.
Important Note! Be cautious with “only” placement; the meaning of the sentence is changed based on its position.
FAQs on Adverbs
What are some common examples of adverbs?
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, offering additional details about how, when, where, or to what extent an action occurs. Some Common examples of adverbs include fastly, quickly, slowly, always, very, and here.
Can Edulearnx give some exercises for adverbs?
We can design adverb exercises by providing a verb and asking you to add an adverb that describes how the action is performed. For example, with the verb “run,” you can create a sentence like “He runs quickly.” Alternatively, you can write a sentence and then rewrite it using a different adverb.
What are the main types of adverbs?
There are several main types of adverbs:
- Adverbs of manner: Describe how an action is performed, such as slowly, quietly, or carefully.
- Adverbs of place: Indicate where an action takes place, like here, there, or everywhere.
- Adverbs of time: Provide information about when an action occurs, such as now, later, or yesterday.
- Adverbs of frequency: Express how often an action occurs, e.g., always, often, or never.
- Adverbs of degree: Show to what extent or how much something happens, like very, quite, or too.
What are adverbs of manner and their use?
Adverbs of manner commonly tell how an action is performed. Examples include “quickly” and “softly.” They enhance sentences by detailing the manner of an action.
How do you identify an adverb?
- Ask Questions (How? When? Where?)
- To what extent? Look for -ly Endings (but not exclusively):
- Examine the Sentence Structure
- Consider Context
- Use Adverb Lists for Reference
 List of Adverbs That Start With P | All Positive & Impactful Adverbs
List of Adverbs That Start With P | All Positive & Impactful Adverbs
 List of Adverbs That Start With O | All Positive & Impactful Adverbs
List of Adverbs That Start With O | All Positive & Impactful Adverbs
 List of Adverbs That Start With N | All Positive & Impactful Adverbs
List of Adverbs That Start With N | All Positive & Impactful Adverbs