In the English language, we categorize every word into a specific type known as a part of speech. The part of speech of a word is defined by its function within a sentence. Parts of speech are groups of words that share similar grammatical roles within phrases and sentences. A complete understanding of these classes is important for effective communication and writing.
There are several different parts of speech each with its characteristics and functions. Let’s get started by explaining parts of speech and how to identify, modify, and use them in simple and complex sentences.
Parts of speech are word categories determined by their grammatical roles in sentences. Functions and meanings organize them. English has ten common parts: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, determiners, and articles. Each serves a distinct role in constructing meaningful and grammatically sound sentences.
Open Word Classes:
Open word classes are dynamic parts of speech that welcome new words. Examples include nouns, verbs, adjectives, interjections, and adverbs.
Closed Word Classes:
Closed word classes are stable parts of speech without new additions. Examples include pronouns, conjunctions, determiners, and prepositions.
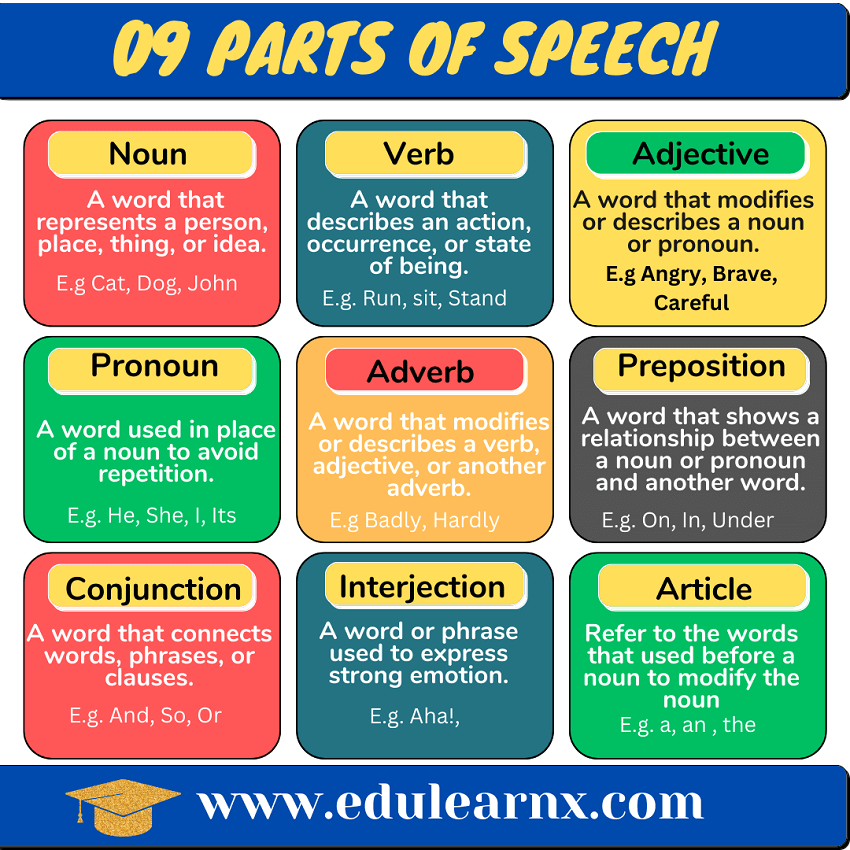
Now, we will closely examine key parts of speech, including the verb, noun, and adjective, to enhance our understanding of sentence formation and the interplay of different linguistic elements. This exploration aims to provide a better understanding of constructing sentences and the functions of individual parts of speech.
A noun indicating a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns may be used with articles like “the,” “a,” or “an.” Proper nouns start with capital letters, while common nouns do not. Nouns can be singular or plural, concrete or abstract nouns, and show possession through the addition of ‘s. They play various roles in a sentence, serving as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, subject complements, or objects of prepositions.
Each of these nouns serves a different purpose, So, we look closely at this.
Examples:
John, Tokyo, computer, Christmas, bird, book, giraffe, park, university, project, dance, beach, Sydney, artist, engineer, Alice, Lisa, Robert, firefighter, Italy, tea, soccer, adventure, laughter, success.
Examples of Nouns in a Sentence:
Types of Nouns
A verb is a word that expresses action or occurrence, for instance, read, run, pick, sit, garnish, come, pitch, etc.
Examples:
Jump, read, think, write, dance, eat, sleep, study, play, create, believe, understand, talk, drive, laugh, run, explore, enjoy, speak, climb.
Sentence Examples:
Types of Verbs
Pronouns are used to substitute nouns in sentences, with various types, such as reflexive, possessive, relative, and indefinite pronouns.
Examples:
I, me, you, he, him, her, it, we, us, they, my, mine, your, its, our, ours, their, theirs, myself, yourself, himself, ourselves, yourselves, which, what, each, either, neither, anyone, nobody, etc.
Sentence Examples:
Types of Pronouns
An adjective is a word used to describe a noun or a pronoun.
Examples:
Green tree, old book, brave soldier, happy child, ice cream, small house, fast car, blue sky, tall mountain, smart student, interesting story, hot coffee, kind person, shiny coin, quiet room, soft pillow.
Adjectives Sentence Examples:
Types of Adjectives
Descriptive Adjectives:
Quantitative Adjectives
Demonstrative Adjectives
Possessive Adjectives
Interrogative Adjectives
Indefinite Adjectives
Proper Adjectives
Ordinal Adjectives
Numeral Adjectives
Comparative Adjectives
Superlative Adjectives
Emphasizing Adjectives
An adverb modifies or further explains an adjective, verb, or another adverb. It provides additional information to enhance clarity and vividly describe details in a sentence. Adverbs typically end in -ly, but exceptions like very and never.
Examples:
Swiftly, soon, greatly, poorly, completely, cautiously, barely, nearly, voraciously, never, rapidly, silently, effectively, truly, almost, etc.
Sentence Examples:
Definition of Determiners
Determiners are important parts of speech that are used to be placed in front of nouns to clarify their reference. They include categories such as:
Examples: a, an, the
E.g., two, eight, ninety-nine, etc.
Examples: his, its, my, their, etc.
Examples: other, the other, another, etc.
E.g., these, those, that, this, etc.
Examples: much, a few, many, some, etc.
E.g. : every, both, each, all, etc.
Examples: such, quite, rather, what
Articles
Articles are a subtype of determiners that act as adjectives identifying nouns. They can be “a,” “an,” or “the.”
Definition: Indicates a known noun to the audience.
Example: I am going to sit in the chair.
Definition: Represents an unfamiliar or first-time mentioned noun.
Example: I am going to sit in a chair.
A conjunction links words, phrases, or clauses, signifying the relationship between the joined elements. Coordinating conjunctions (but, or, and, nor, for, so, yet) connect grammatically equal elements. Subordinating conjunctions (because, although, while, since, etc.) link clauses of unequal grammatical status.
Examples:
Before, after, but, either, because, however, or, since, neither, so, still, unless, and, etc.
Sentence Examples:
A preposition in English shows a relationship between two words or phrases.
Examples:
In, at, on, about, after, before, since, with, near, from, upon, toward, along, above, between, according to, except.
Preposition Sentence Examples:
An interjection is like an exclamation. It expresses emotion, reaction, or excitement. It stands alone in a sentence and doesn’t connect grammatically to other parts of the sentence.
Examples:
Ahem!, aha!, aw!, eh!, gosh!, great!, hey!, hi!, hi!, hooray!, oh!, oh!, oops!, ouch!, phew!, well!, yeah!
Sentence Examples:
In sentence construction parts of speech are found in clauses which are word groups containing a subject and a verb. The verb is also a component of a complete verb phrase known as a predicate.
Simple or Basic Sentences
In its simplest form, a sentence may consist of one independent clause.
For Example: “She reads a fascinating book.” contains one clause.
The complete sentence “She reads a fascinating book” is an independent clause, expressing one subject performing one action, and it is classified as a simple sentence.
Recognize that nouns and pronouns frequently serve as subjects or objects in simple sentences, while verbs express actions. Reviewing the example:
Complex Sentences
Note that complex sentences involve an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. Conjunctions like “because,” “since,” “which,” or “who” connect these clauses. For instance: “She reads a fascinating book because she wants to learn”.
She (subject, pronoun) reads (verb) a (article) fascinating (adjective) book (object, noun) because (conjunction) she wants (verb) to learn (infinitive).
Here are a few exercises for you to practice Parts of Speech:
A). In the sentence “She sang beautifully,” what part of speech is the word “beautifully”?
B). Identify the part of speech for the word “happiness” in the sentence “Her happiness was contagious.”
C). In the sentence “He swiftly completed the task,” what part of speech is the word “swiftly”?
D). Determine the part of speech for the word “underneath” in the sentence “The cat hid underneath the bed.”
E). In the sentence “The team celebrated their victory joyfully,” what part of speech is the word “joyfully”?
F). Identify the part of speech for the word “excellent” in the sentence “She received an excellent grade.”
G). In the phrase “to the moon,” what part of speech is the word “to”?
H). Determine the part of speech for the word “both” in the sentence “They both arrived on time.”
I). In the sentence “He whispered a secret to her,” what part of speech is the word “whispered”?
J). Identify the part of speech for the word “unbelievably” in the sentence “She ran unbelievably fast.”
Answers: A) 1, B) 1, C) 3, D) 1, E) 2, F) 3, G) 1, H) 1, I) 2, J) 2